
本研究室では「化学工学」、「界面科学」および「機械学習」をベースに、「医用工学」および「界面プロセス工学」分野の研究を行っています。
Our laboratory conducts research in the fields of Biomedical Engineering and Interfacial Process Engineering, based on the foundations of Chemical Engineering, Interfacial Science, and Machine Learning.
「医用工学」分野:新規な創傷被覆材(傷を覆って治癒を促すもの)などの医療機器の開発や未来の医療である再生医療分野で重要な生体組織の新規再生方法の開発研究を行っています。
「界面プロセス工学」分野:様々な分野で使用されているカプセルの新規作製法やエマルションの安定化法の開発研究を行っています。
Biomedical Engineering: We are engaged in the development of novel medical devices, such as advanced wound dressings (materials that cover wounds and promote healing), as well as research into innovative methods for regenerating biological tissues, which play a crucial role in the future field of regenerative medicine.
Interfacial Process Engineering: We conduct research on new methods for fabricating capsules and stabilizing emulsions, both of which are widely used across various industries.
本研究室発のスタートアップ企業(代表取締役:武井孝行)をとおして開発品の社会実装化を精力的に進めており、産・学の両面の経験ができる研究室です。
Through a startup company originating from our laboratory (CEO: Takayuki Takei), we are actively promoting the social implementation of our research outcomes. This enables students to gain experience in both academia and industry within our laboratory.
【キーワード (Keywords)】
医用工学 (Biomedical Engineering):
ヒドロゲル (Hydrogel)、バイオマテリアル (Biomaterials)、ドラッグデリバリーシステム(DDS)、毛細血管網 (Blood capillary network)、再生医療 (Regenerative medicine)
界面プロセス工学 (Interfacial Process Engineering):
エマルション (Emulsion)、カプセル (Capsules)、界面化学 (Interfacial Science)、Hansen溶解度パラメーター (Hansen Solubility Parameter)、機械学習 (Machine Learning)、ベイズ最適化 (Bayesian Optimization)
医用工学 (Biomedical Engineering)
キトサンゲル
(Chitosan hydrogel)
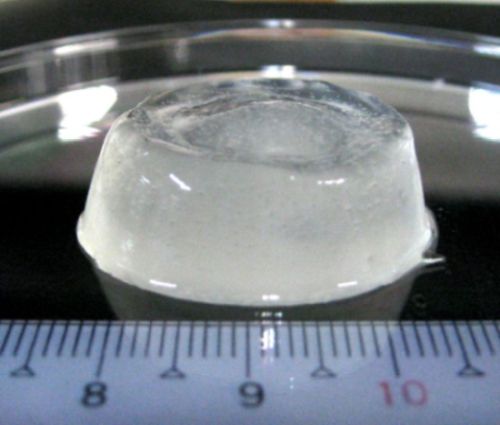

キトサンは止血効果や抗菌効果、創傷治癒促進効果を有する機能性天然高分子です。本研究室では生体安全性の高いキトサンゲルを開発しています。実際にヒト臨床試験により、上市されている他の創傷被覆材よりも創傷の治癒促進効果が高いことを実証しています。現在、薬事申請等により上市を目指しています。
Chitosan is a functional natural polymer with high hemostatic, antibacterial, and wound-healing promoting effects. We developed chitosan hydrogel with high biological safety. In fact, human clinical trials have demonstrated that the hydrogel is more effective in promoting wound healing than other wound dressings on the market. The pharmaceutical application in Japan is in progress.
疎水化高分子からなるゲル
(Hydrophobically-modified polymer hydrogel)
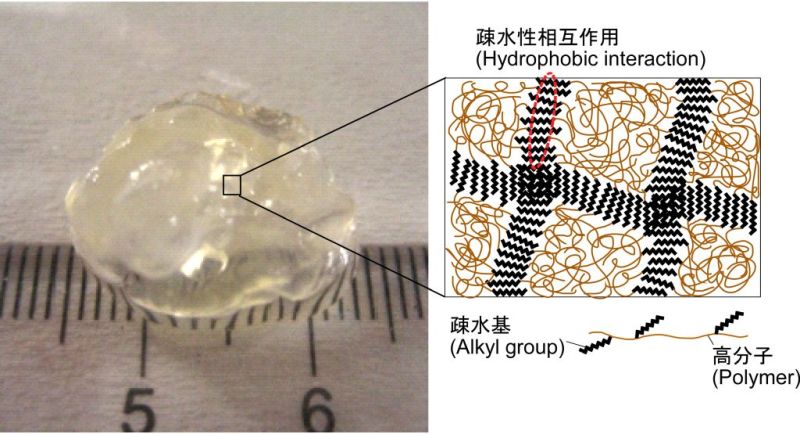
生体毒性の高い化学架橋剤で高分子を架橋することで得られるヒドロゲルは、その残存する化学架橋剤により医療への応用は不適です。本研究室では、高分子に疎水基を導入することで、化学架橋剤を使用することなくヒドロゲルを作製できることを見出しました。これは、ヒドロゲルなどの水環境下では疎水性相互作用が強く働くことを応用したゲル作製法です。
Hydrogels cross-linked with toxic chemicals are not suitable for medical applications due to the residual chemicals in the hydrogels. We found hydrophobically-modified polymers form hydrogels without using toxic chemicals. The cross-linking points of the polymers would be formed by hydrophobic interaction between hydrophobic groups incorporated into the polymers.
毛細血管網の再現
(Creation of blood capillary network)
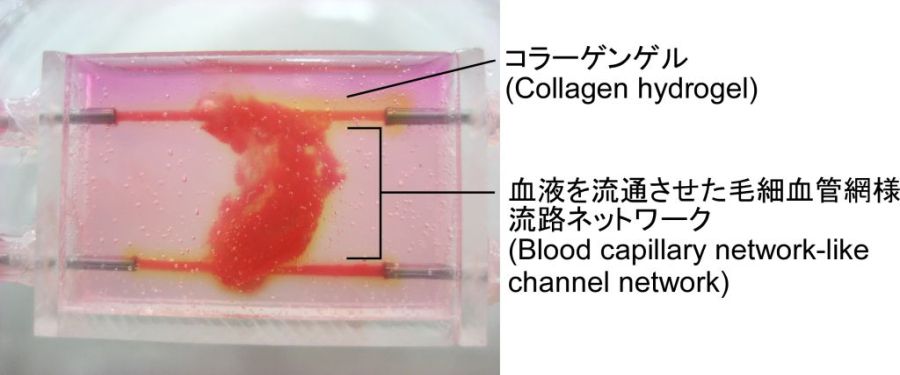
再生医療の最終目標は、生体外で生体組織を作り出すことです。そのためには生体の緻密な毛細血管網を再現できる技術が必要です。本研究室では、“綿飴”状のマイクロファイバーの束を血管の鋳型として利用することで、従来法よりも短時間で緻密な毛細血管網用の流路ネットワークを作製できる技術を開発しました。
The goal of regenerative medicine is to create tissues and organs in vitro. To achieve this goal, a technology that can reproduce the dense capillary network of a human body is necessary. We developed a technology that can fabricate a dense capillary network in a shorter time than conventional methods by using "cotton candy"-like microfibers as a template for the capillary network.
界面プロセス工学 (Interfacial Process Engineering)
気相中での新規カプセル作製法
(Preparation of capsules in gas phase)
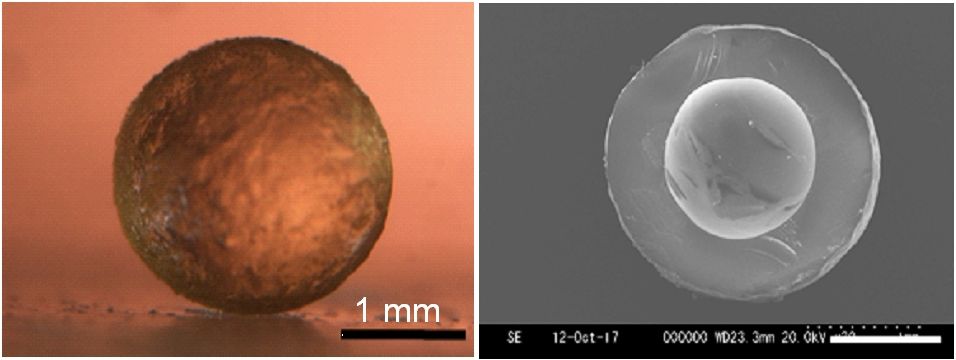
有価物質をカプセル内に封入することでその物質を外部環境から保護できるなどの多くのメリットが生じます。一般的にカプセルは液相中で調製されます。本研究室では、撥液物質を利用した気相中での新規なカプセル調製法を開発しました。本法では有価物質をロスすることなくカプセル内に封入することができます。また、真球かつ壁厚みの均一なコア-シェルカプセルを連続的に調製できるため、社会実装が期待されます。
Encapsulating ingredients in capsules provides a number of advantages, including protection of the ingredients from external environment. Generally, capsules are prepared in the liquid phase through emulsion. We developed a unique method to prepare capsules in the gas phase using liquid repellent materils (e.g. superamphiphobic plates, powder and liquid marbles). This method can encapsulate ingredients without loss. Moreover, core-shell capsules with spherical and uniform wall thickness can be continuously produced.
ベイズ最適化を利用したカプセルやエマルション調製条件の効率的最適化
(Efficient optimization of capsule and emulsion preparation conditions using Bayesian optimization)
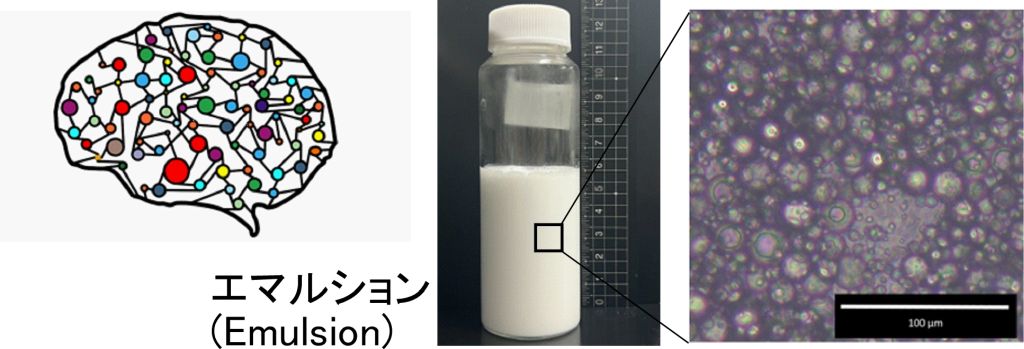
目的の物性を有するカプセルやエマルションを作製するためには、種々のパラメーター(界面活性剤濃度など)の最適化が必要です。パラメーターが無数に存在する場合、その最適化は極めて困難であり、かつ時間がかかります。本研究室では機械学習の1つであるベイズ最適化により、カプセルやエマルション調製条件の効率的最適化に取り組んでいます。実際に、従来では100パターン以上のパラメーターの組み合わせで実験をして最適値を求めてましたが、ベイズ最適化を適用することにより最適化に必要な実験数を1/5にまで減らすことができてます。
Optimization of various parameters (e.g., surfactant concentration) is necessary to prepare capsules and emulsions with the desired physical properties. When there are huge number of parameters, optimization is extremely difficult and time-consuming. We have used Bayesian optimization (one of machine learning methods) for efficient optimization of capsule and emulsion preparation conditions. In fact, the number of experiments required for optimization could be reduced to 1/5 by applying Bayesian optimization, compared with convential methods.
